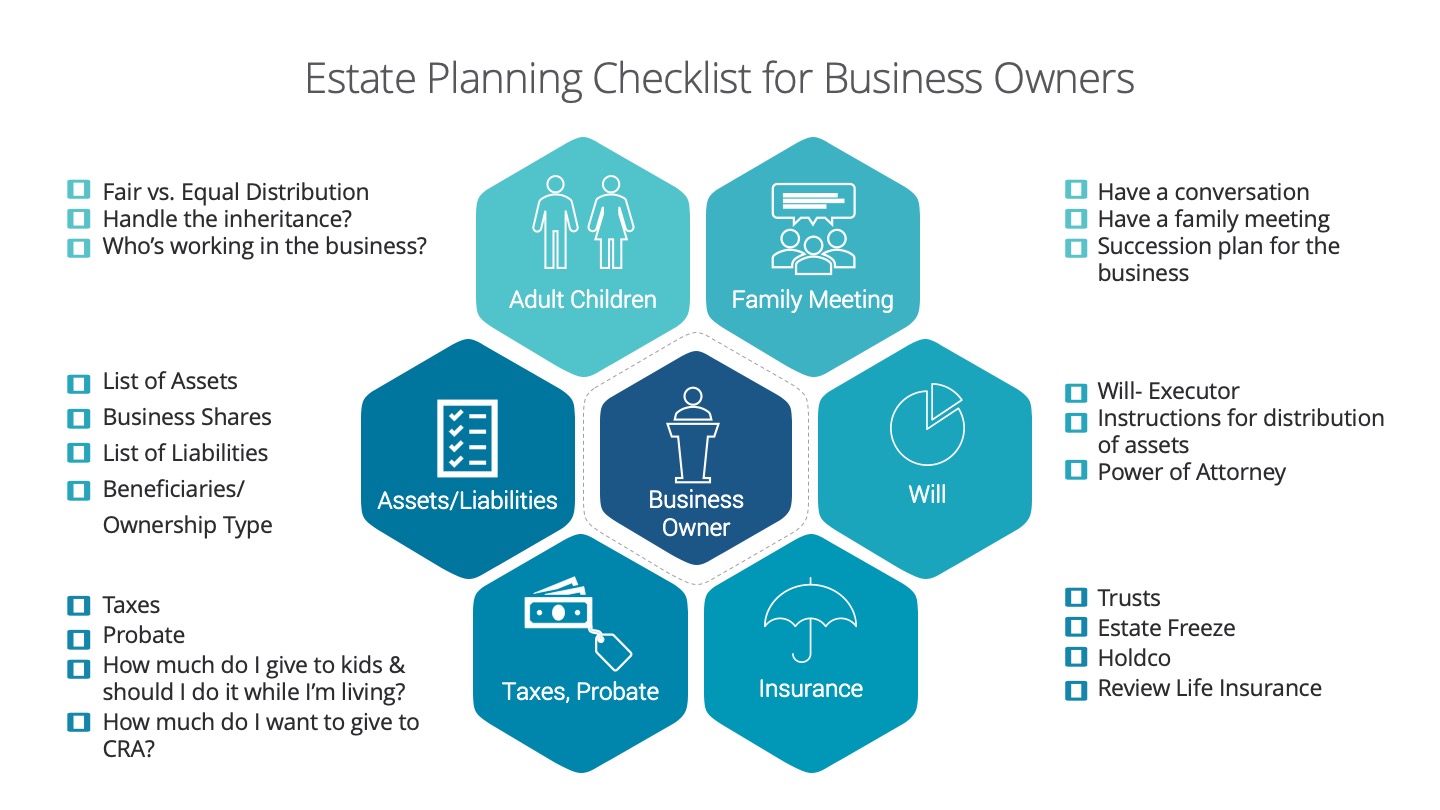
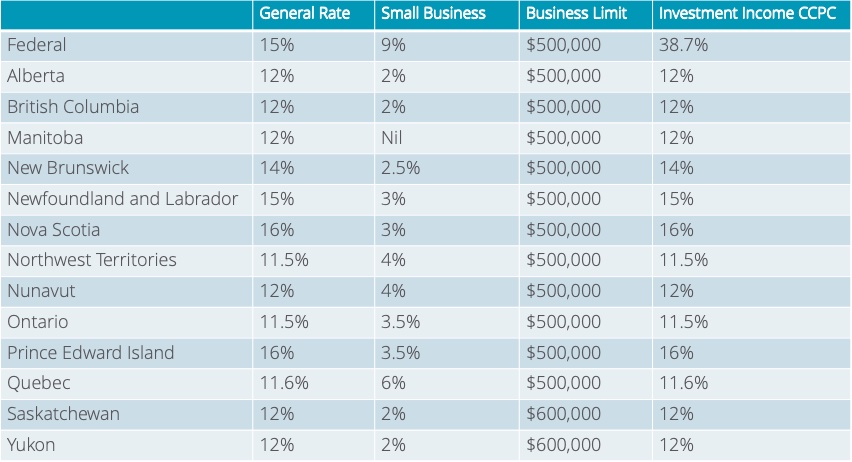
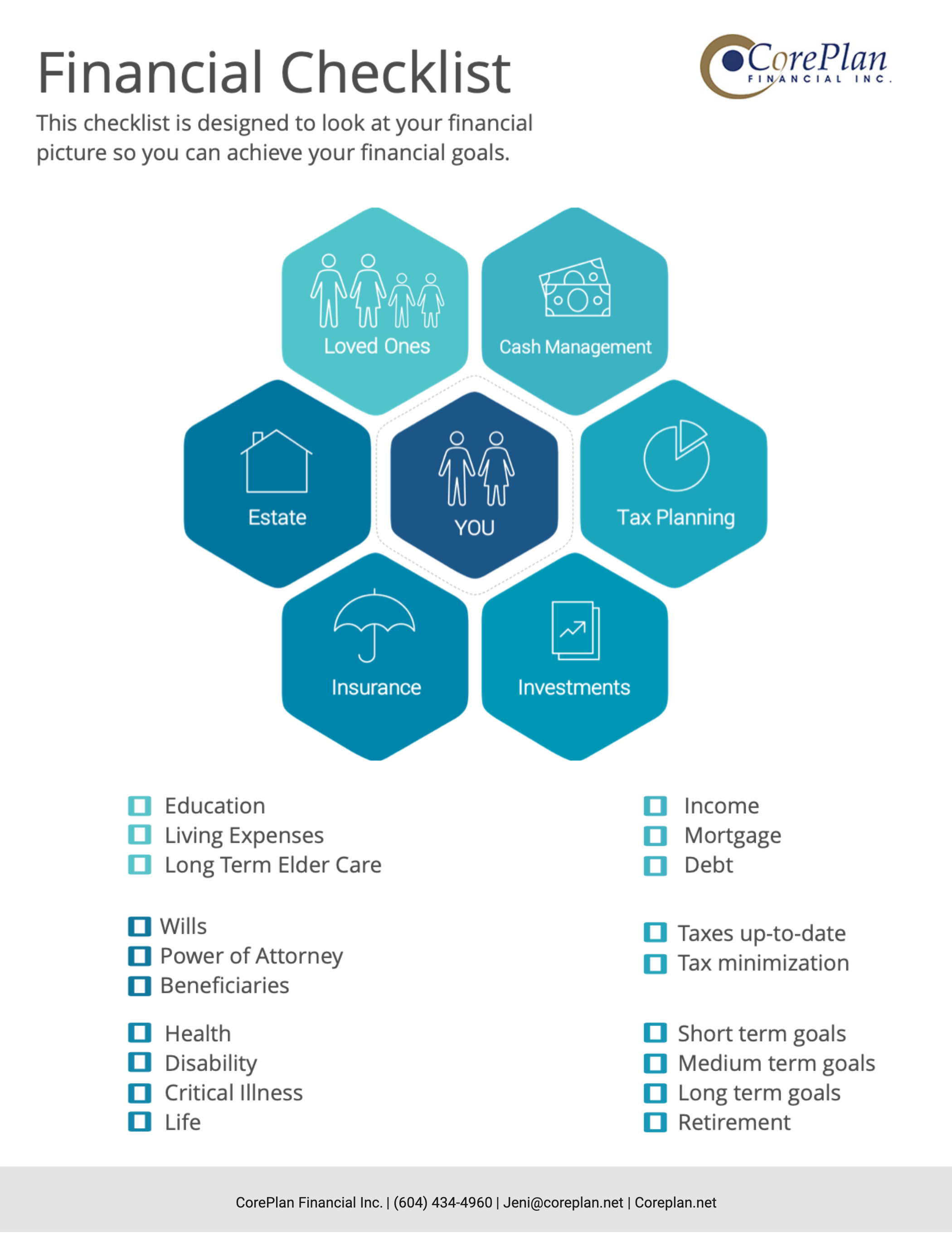
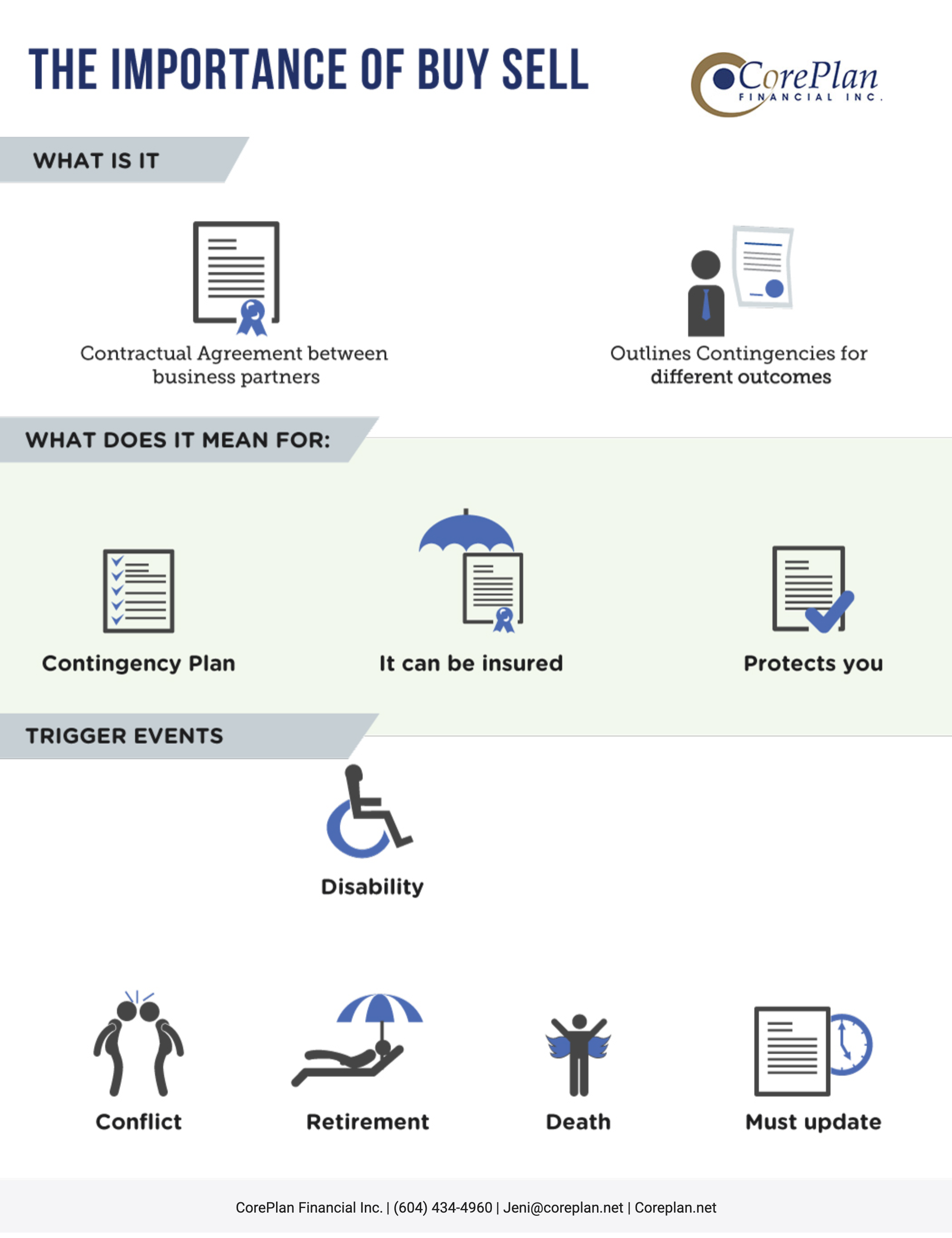
2019 Tax Tips for Employees
Now that we are nearing year end, it’s a good time to review your finances. With the federal election over and no major tax personal tax changes for this year, 2019 is a good year to make sure you are effectively tax planning. Below, we have listed some of the key areas to consider and provided you with some useful guidelines to make sure that you cover all of the essentials. We have divided our tax planning tips into 4 sections:
-
Tax deadlines
-
Family tax issues
-
Managing your investments
-
Retirement planning
Tax Deadlines for 2019 Savings
December 31, 2019:
-
If you reached the age of 71 in 2019, contributions to your RRSP
-
Use up your TFSA contribution room
-
Contribute to RESP to get the Canadian education savings grant and the income-tested Canada learning bond.
-
Contribute to RDSP to get the Canada disability savings grant and the income-tested Canada disability savings bond.
-
Medical expenses
-
Investment counsel fees, interest and other expenses relating to investments
-
Some payments for child and spousal support
-
Fees for union and professional memberships
-
Student loan interest payments
-
Deductible legal fees
-
Charitable gifts
-
Political contributions
January 30, 2020:
-
Interest on intra-family loans
-
Interest you must pay on employer loans, to reduce your taxable benefit
February 29, 2020:
-
Contributions to provincial labour-sponsored venture capital corporations
-
Deductible contributions to a personal or spousal RRSP
-
RRSP Repayment under Home Buyers Plan or Lifelong Learning Plan

Family Tax Issues
Check your eligibility to the Canada Child Benefit
In order to receive the Canada Child Benefit in 2020/21, you need to file your tax returns for 2019 because the benefit is calculated using the family income from the previous year. Eligibility depends on set criteria such as your family’s income and the number and age of your children and you may qualify for full or partial amount.
Consider family income splitting
The CRA offers a low interest rate on loans and it therefore makes sense to consider setting up an income splitting loan arrangements with members of your family, whereby you can potentially lock in the family loan at a low interest rate of 2% and subsequently invest the borrowed monies into a higher return investment and benefit from the lower tax status of your family member. Don’t forget to adhere to the Tax on Split Income rules.
Contribute to Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP)
The Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) is a savings plan for parents and others to save for a child’s education. The Canada education savings grant (CESG) will match up to 20% of contributions up to $2,500. That means the CESG can add a maximum of $500 to an RESP each year. Grant room accumulates until the child turns 17, therefore unused basic CESG amounts for the current year are carried forward for possible use in the future years. The income-tested Canada learning bond (CLB) is paid directly to the RESP by the Canadian government to low-income families. There are no personal contributions required to receive the CLB.
Contribute to Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP)
The Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) is a savings plan for parents and others to save for the financial security of a person who is eligible for the disability tax credit (DTC). The Canada disability savings grant will pay matching grants of 300%, 200% or 100% depending on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and amount contributed. The income-tested Canada disability savings bond is paid directly to the RDSP by the Canadian government to low- income Canadians with disabilities. Before December 31 of the year you turn 49 years old, you can carry forward up to 10 years of unused grant and bond entitlements to future years, as long as you met the eligibility requirements during the carry forward years.
Managing Your Investments
Use up your TFSA contribution room
If you are able, it’s worth contributing the full $6,000 to your TFSA for 2019. You can also contribute more (up to $63,500) if you are 28 or older and haven’t made any previous TFSA contributions.
Contribute to Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP)
The Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) is a savings plan for parents and others to save for a child’s education. The Canada education savings grant (CESG) will match up to 20% of contributions up to $2,500. That means the CESG can add a maximum of $500 to an RESP each year. Grant room accumulates until the child turns 17, therefore unused basic CESG amounts for the current year are carried forward for possible use in the future years. The income-tested Canada learning bond (CLB) is paid directly to the RESP by the Canadian government to low-income families. There are no personal contributions required to receive the CLB.
Contribute to Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP)
The Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) is a savings plan for parents and others save for the financial security of a person who is eligible for the disability tax credit (DTC). The Canada disability savings grant will pay matching grants of 300%, 200% or 100% depending on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and amount contributed. The income-tested Canada disability savings bond is paid directly to the RDSP by the Canadian government to low- income Canadians with disabilities. Before December 31 of the year you turn 49 years old, you can carry forward up to 10 years of unused grant and bond entitlements to future years, as long as you met the eligibility requirements during the carry forward years.
Donate securities to charity
Make a donation by year end will provide you tax savings. If you donate eligible securities or mutual funds, capital gains tax does not apply, and you can receive a tax receipt for their full market value. Also, the charity gets the full value of the securities.
Think about selling any investments with unrealized capital losses
It might be worth doing this before year-end in order to apply the loss against any net capital gains achieved during the last three years. Any late trades should ideally be completed on or prior to December 24, 2019 and subsequently confirmed with your broker.
Conversely, if you have investments with unrealized capital gains which are not able to be offset with capital losses, it may be worth selling them after 2019 in order to be taxed on the income the following year.
Consider the timing of purchasing of certain non-registered investments
If you are considering purchasing an interest-bearing investment like a guaranteed investment certificate (GIC) with a maturity date of one year or more, you may consider delaying the purchase to the following year, so you don’t have to pay tax on accrued interest until 2021. You should also consider this with mutual funds that make taxable distributions before the end of 2019, consider delaying this until early 2020. Don’t pay taxes earlier than necessary.
Check if you have investments in a corporation
The new passive investment income rules apply to tax years from 2018. They state that the small business deduction is reduced for companies which are affected with between $50,000 and $150,000 of investment income, therefore the small business deduction has been stopped completely for corporations which earn passive investment income of more than $150,000. At a provincial level, Ontario and New Brunswick have indicated that they are not following the federal rules to limit access to the small business deduction.
Retirement Planning
Make the most of your RRSP
The deadline for making contributions to your RRSP for the year 2019 is February 29, 2020. There are three things that affect how much you may contribution towards your RRSP, as follows:
-
18% of your previous year’s earned income
-
Up to a maximum of $26,500 for 2019 and $27,230 for 2020
-
Your pension adjustment
Remember that deducting your RRSP contribution reduces your after-tax cost of making said contribution.
Check when your RRSP is due to end
You should wind-up your RRSP if you reached the age of 71 during 2019 and your final contributions should be made by December 31, 2019.
Convert to RRIF before year end
If you’re 65 or older in the year, you’re entitled to a pension credit that can fully or partly offset the tax on the first $2,000 of eligible income annually. Consider setting up a RRIF before year-end to pay out $2,000 annually if you don’t have any other eligible pension income.
Contact us if you have any questions, we can help.