Tax Tips for Filing Your 2024 Income Tax Return
The deadline for filing your 2024 income tax return is April 30, 2025. Stay informed about the latest tax changes and benefits available to maximize your savings and ensure compliance. This guide outlines the key updates and important deductions and credits separated into sections for Individuals and Families, and Self-Employed Individuals.
For Individuals and Families
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
-
Increased minimum tax rate and basic exemption threshold.
-
Modified calculation for adjusted taxable income affecting foreign tax credits and minimum tax carryovers.
-
Limited value on most non-refundable tax credits.
Canada Pension Plan (CPP) Enhancement
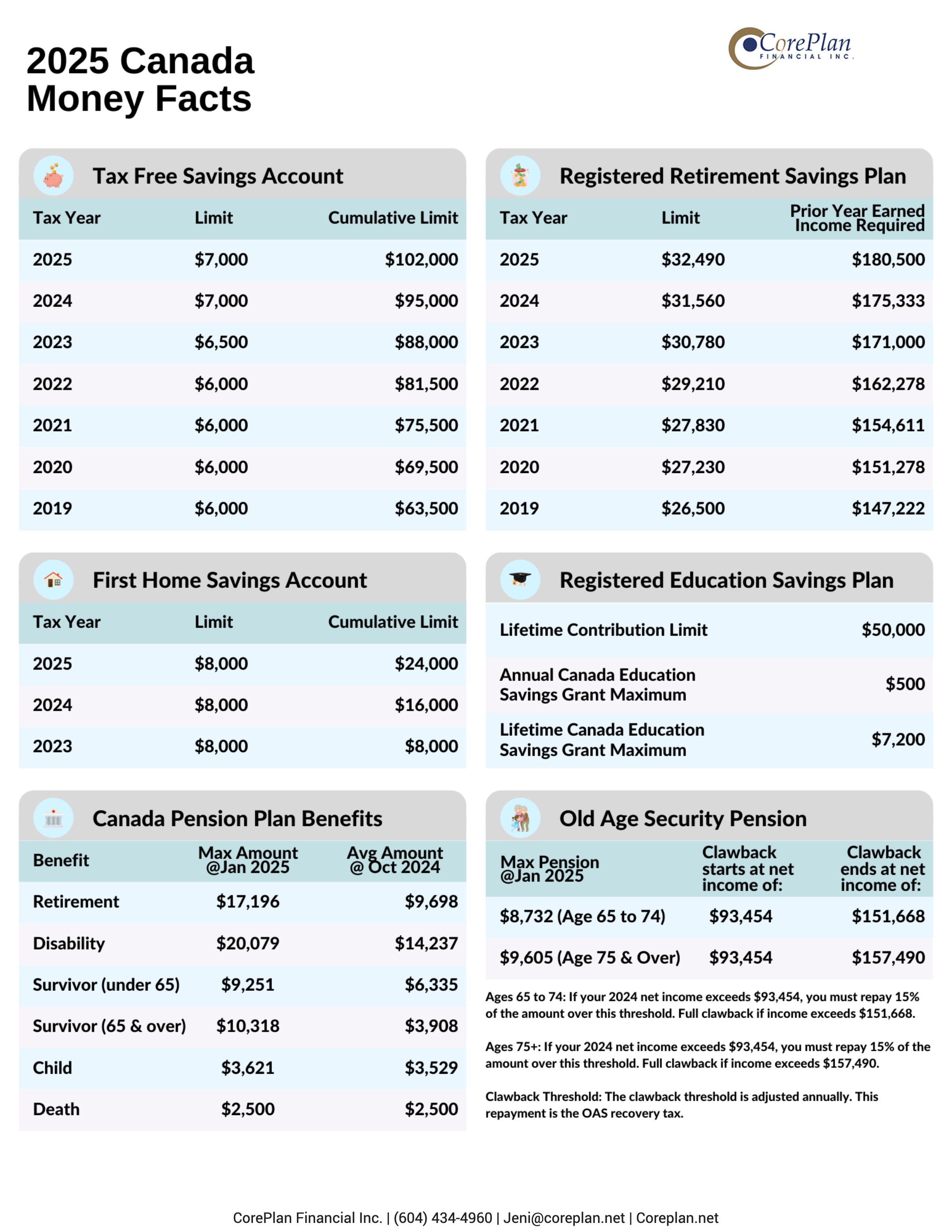
• The standard CPP contribution rate remains at 5.95% for both employees and employers on earnings up to $68,500 (the Year’s Maximum Pensionable Earnings or YMPE) in 2024.
• Additionally, employees and employers each contribute an extra 4% on earnings between the YMPE ($68,500) and the Year’s Additional Maximum Pensionable Earnings (YAMPE) of $73,200 in 2024.
Home Buyers’ Plan (HBP)
-
Withdrawal limit increased from $35,000 to $60,000 after April 16, 2024, with temporary repayment relief available.
Volunteer Firefighters and Search and Rescue Volunteers
-
Amounts increased from $3,000 to $6,000 for eligible individuals completing at least 200 hours of combined volunteer service.
Basic Personal Amount (BPA)
• For 2024, the Basic Personal Amount (BPA) has increased to $15,705 for taxpayers with net income up to $173,205.
• For taxpayers with net incomes above this amount, the BPA is gradually reduced, reaching a minimum of $14,138 at incomes of $235,675 or higher.
Short-term Rentals
-
Expenses related to non-compliant short-term rentals are no longer deductible after January 1, 2024.
Popular Tax Credits and Deductions
Canada Training Credit (CTC) Eligible taxpayers aged 26 to 65 can claim this refundable tax credit to cover a portion of eligible tuition and fees for training or courses to enhance their skills.
Canada Caregiver Credit (CCC) This non-refundable tax credit supports individuals caring for family members or dependents with a physical or mental impairment. The amount varies based on the dependent’s relationship, net income, and circumstances.
Child Care Expenses Child care expenses, such as daycare, nursery schools, day camps, and boarding schools, are deductible if incurred to enable a parent or guardian to work, pursue education, or conduct research.
Disability Tax Credit (DTC) The DTC provides a non-refundable tax credit for individuals with disabilities or their caregivers to reduce the amount of income tax payable. Applicants must have a certified disability lasting at least 12 months.
Moving Expenses Deductible moving expenses include transportation and storage costs, travel expenses, temporary living costs, and incidental expenses incurred when relocating at least 40 kilometers closer to a new work location, educational institution, or business location.
Interest Paid on Student Loans Interest paid on eligible student loans can be claimed as a non-refundable tax credit. The loans must be under federal, provincial, or territorial student loan programs.
Donations and Gifts Donations made to registered charities or other qualified organizations qualify for non-refundable federal and provincial tax credits. Typically, you can claim eligible amounts up to 75% of your net income.
GST/HST Credit The GST/HST credit is a quarterly refundable payment designed to offset the impact of sales tax on low to moderate-income individuals and families. Eligibility is automatically assessed based on your annual tax return.
For Self-Employed Individuals
CPP Contributions
-
Enhanced CPP contribution rate for self-employed individuals.
Filing and Payment Deadlines
-
Tax Return Deadline: June 16, 2025 (June 15 is Sunday).
-
Balance due must be paid by April 30, 2025.
Reporting Business Income
-
Report income on a calendar-year basis for sole proprietorships and partnerships.
Digital Platform Operators
-
New reporting rules requiring platform operators to collect and report seller information.
Mineral Exploration Tax Credit
-
Eligibility extended for flow-through share agreements signed before April 2025.
Need Assistance?
If you’re unsure about your eligibility for specific credits or deductions, reach out to your tax consultant or tax advisor for personalized guidance. They can help you optimize your tax return, maximize your savings, and ensure compliance with CRA regulations.
Sources
-
Canada Revenue Agency. “What’s New for the 2024 Tax-Filing Season.” Canada.ca, Government of Canada, www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/services/tax/individuals/topics/about-your-tax-return/tax-return/completing-a-tax-return/whats-new.html
-
Canada Revenue Agency. “Maximum Pensionable Earnings and Contributions for 2024.” Canada.ca, Government of Canada, www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/news/newsroom/tax-tips/tax-tips-2023/maximum-pensionable-earnings-contributions-2024.html
-
“7 Biggest Tax Changes Canadians Need to Know in 2025.” TurboTax Canada, Intuit, turbotax.intuit.ca/tips/7-biggest-tax-changes-canadians-need-to-know-in-2025?srsltid=AfmBOoq7eGj8qrkZ6vLpu4Cogfkln4e7PFGD3aYMrdADQ4za4cbHxo5F
-
“Popular Canadian Tax Benefits, Deductions and Credits in 2023.” TurboTax Canada, Intuit, turbotax.intuit.ca/tips/popular-canadian-tax-benefits-deductions-and-credits-in-2023-14180
-
“Personal Tax: What’s New for the 2024 Tax Year.” CPA Canada, Chartered Professional Accountants Canada, www.cpacanada.ca/news/Accounting/Tax/personal-tax-2024
-
Canada Revenue Agency. “Basic Personal Amount.” Canada.ca, Government of Canada, www.canada.ca/en/revenue-agency/programs/about-canada-revenue-agency-cra/federal-government-budgets/basic-personal-amount.html